W13 Kubernetes 1/3
13주차부터 진행되었던 쿠버네티스의 학습 내역을 정리하였습니다.
쿠버네티스 예습, Kubernetes Crash Course for Absolute Beginners
0:00 - Intro and Course Overview
Overview
Part 1. Introdunction to k8s
- What is k8s
- why do we need it.
- why did it become polular.
- k8s Architecture
- How they works in background
Part 2. Main k8s Components
- Pod
- Volume
- Service
- Ingress
- ConfigMap
- Deployment
- Secret
- StatefulSet
- DaemonSet
Part 3. Local Setup
Part 4. Demo Project
k8s is very popular & complex
1:44 - What is Kubernetes
Official def. of k8s
- Open source container orchestration tool
- Devoped by Google
- Helps manage containerized apps in diffrent deploy environment.
What prbls k8s solves?
What are the tasks of an orch. tools?
- Neeed for con. orch. tool
- Trend from Monolith to Microservices.
- Increase usage of (small,independent) con.
- Demand for a proper way of managing those hunds of con.
What features orch tools offer?
- High Availability or no downtime
- Scalability or high performance
- Disaster recovery - backup&restore
4:33 - Kubernetes Architecture
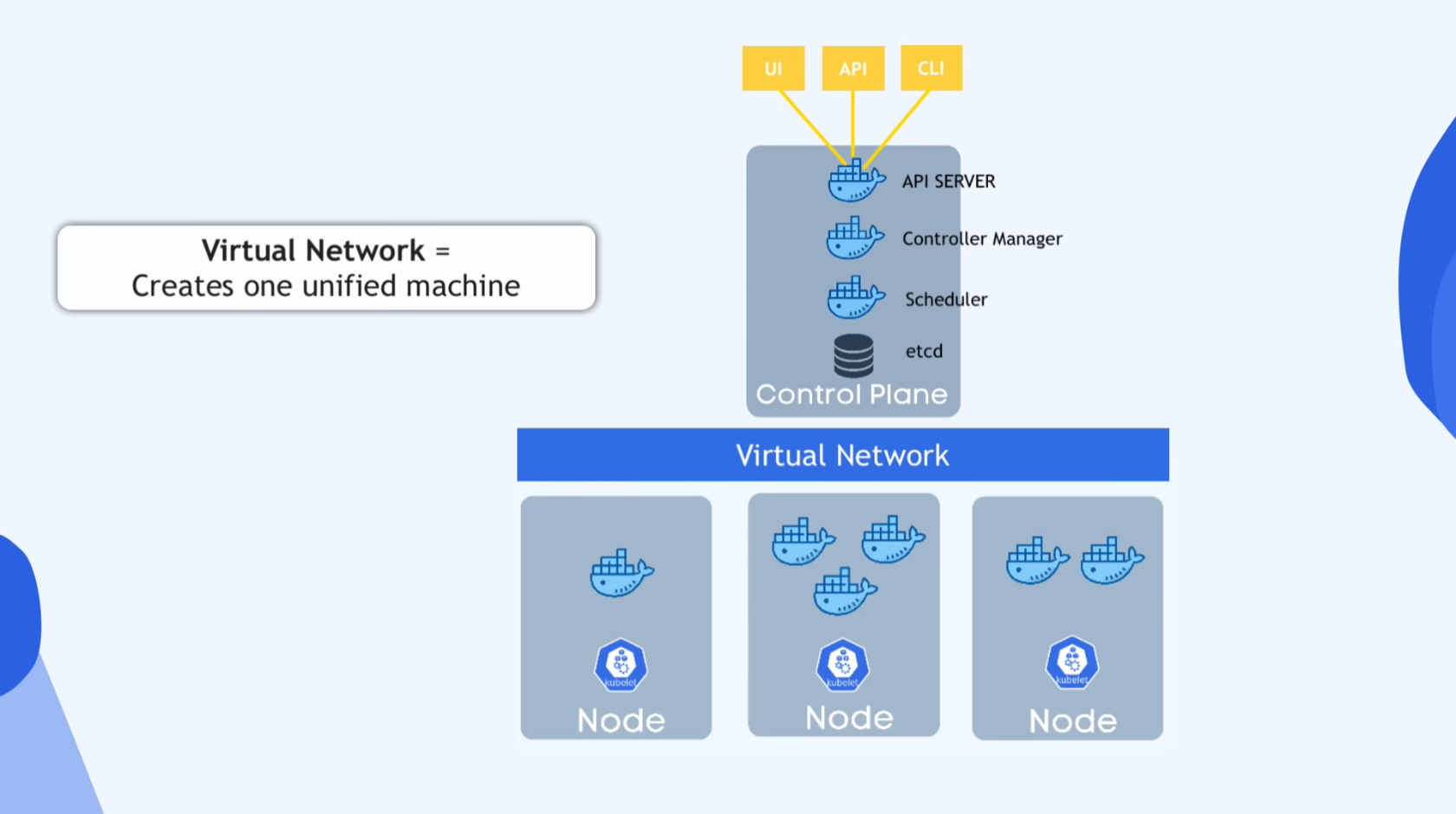
at least one Master node (Virtual/Physical)
- several k8s processes
- necessary to run&manage the cluster
- API server
- Entrypoint to k8s cluster
- UI: Dashboard, etc
- API: scripts&automating
- CLI
- Entrypoint to k8s cluster
- Controller Manager
- Keep track of happenings in cluster
- Scheduler
- ensures Pods placement
- Scheduler decides on which node new pod should be scheduled based on Load
- etcd storage
- k8s backing store
Virtual Network
- Master and Workers talks on N/W
- Creates 1 unified mach. inside of a cluster
several Worker nodes
- a kubelet process
- kubelet: k8s process that communic8s each nodes&excutes some commands
- containers of diffrent apps
- the place that apps r running
| Master | Worker |
|---|---|
| small master processes | Higher workload |
| IMPORTANT | bigger&more resources |
| Need Redundance | - |
8:58 - Main K8s Components
09:29 - Node & Pod
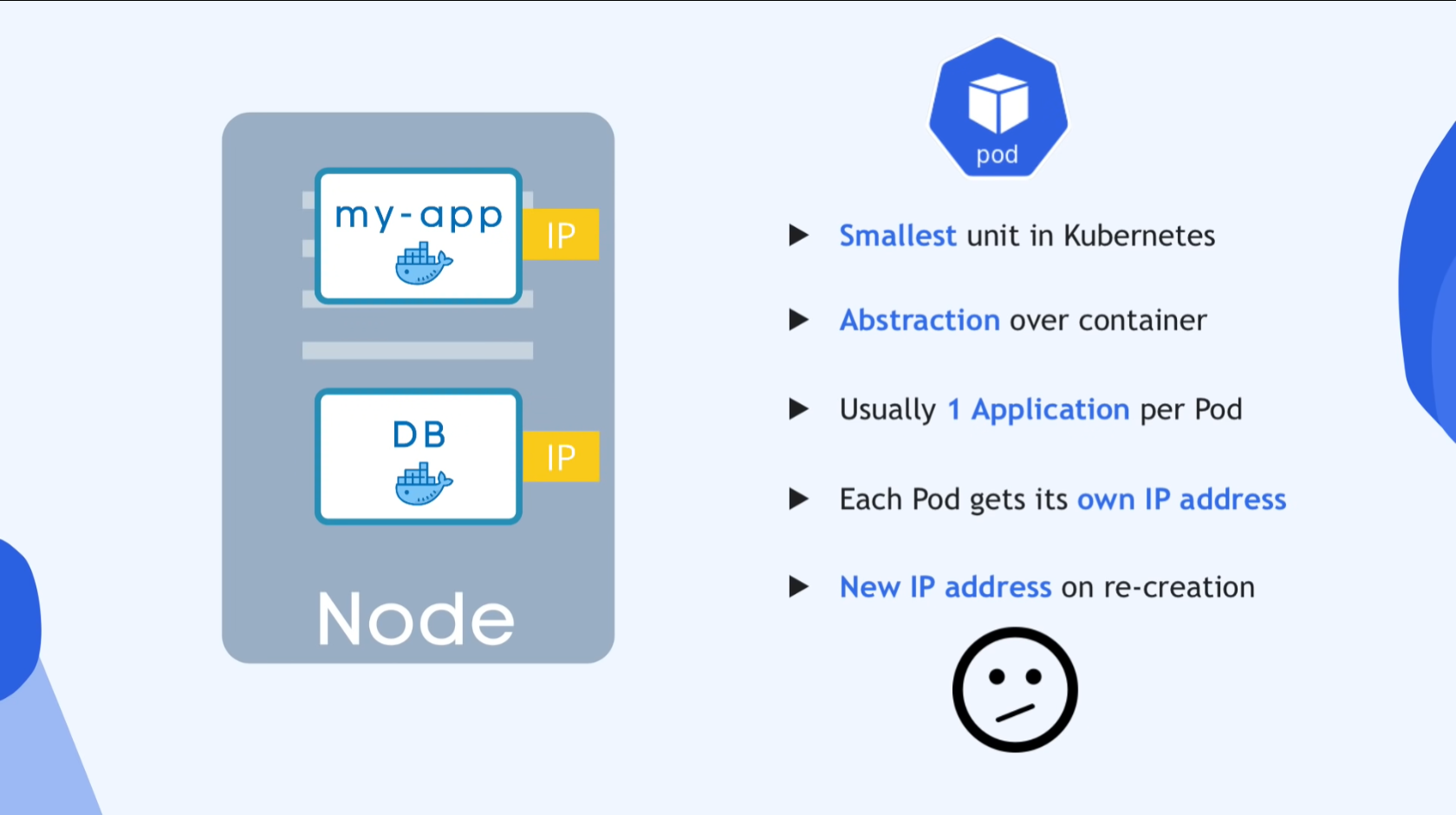
Pod
- Smallest unit in k8s
- Abstraction over container
- Top layer of image
- Usually 1 app per Pod
- Each Pod get its own IP addr
- talks using internal IP
- Ephemeral
- New IP addr on re-creation
- Inconvenient based on IP structure
12:19 - Service & Ingress
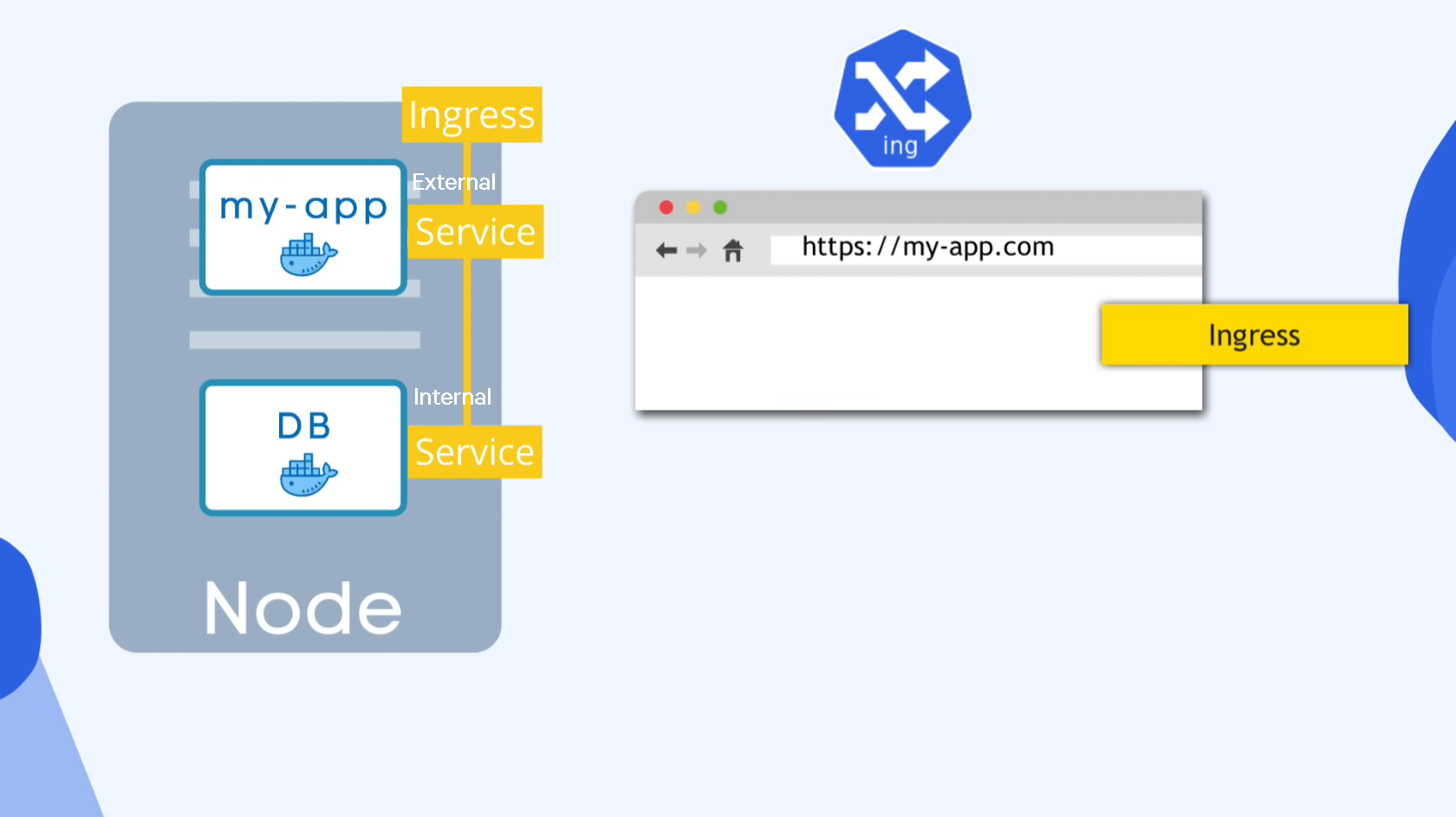
Service
- Permanent IP addr
- Lifecycle of Pod and Service NOT CONNECTED
- Specify the type of Service on creation
- Internal Service = Default
- External Service
- user can access app on web browser
- Internal Service
- user cannot access db
Ingress
- node-ip:port 주소 형식은 실제 사용엔 무리가 있음
- 일종의 도메인서버역할인듯?
- my-app.com 식으로 전환
14:31 - ConfigMap & Secret
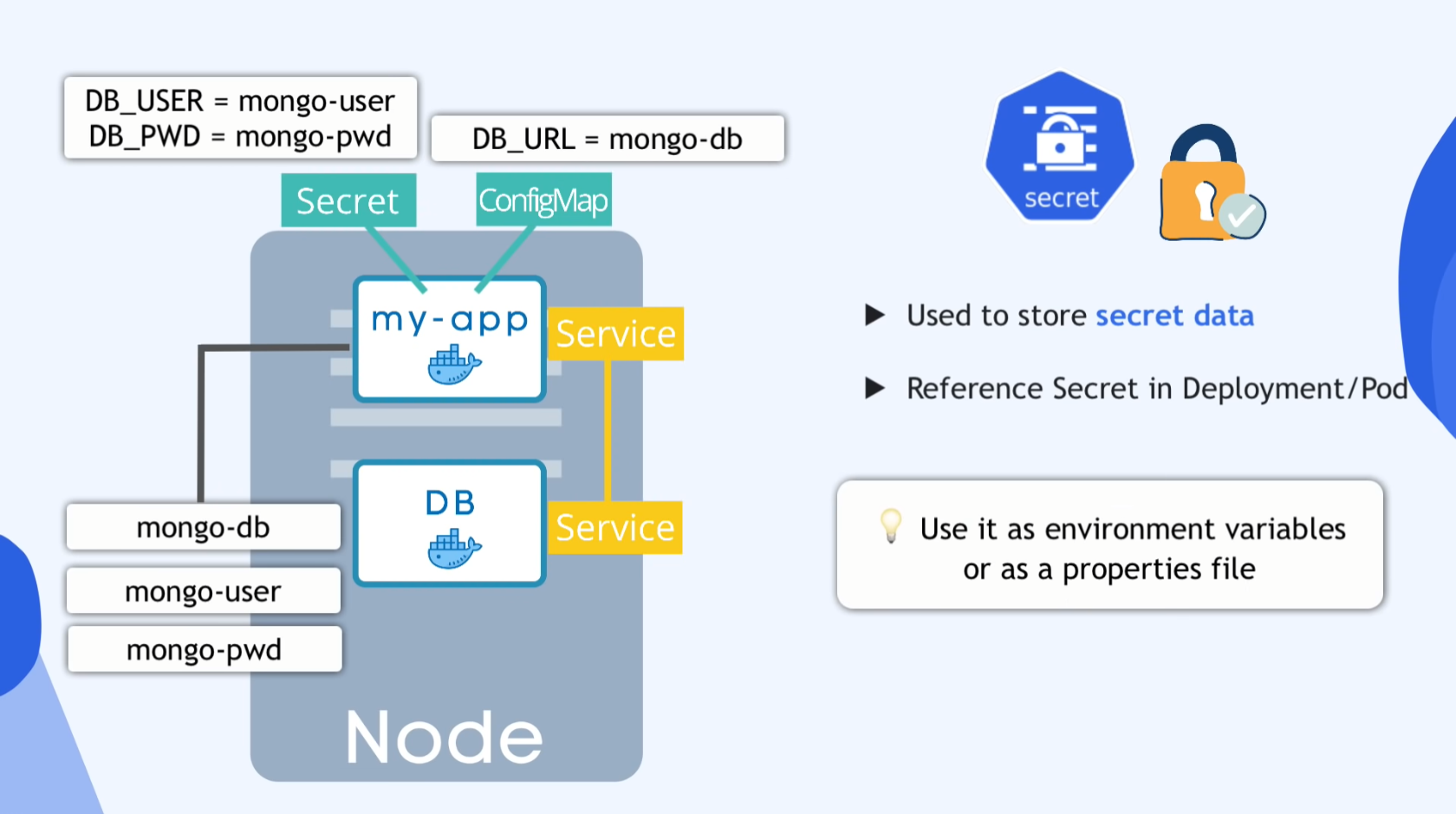
Database URL usually in the BUILT apps
- If u change the DB Endpoint
- Rebuild the image
- Push it to repo
- Pull it in Pod
- Restart whole procedure
ConfigMap
- External conf. of apps
- DB_URL
- DB Servicename
- DB username
- DB password
- ConfigMap is for non-credential data only!
Secrets
- Used to store secret data
- Reference Secret in Deployment/Pod
Use it as environment variables or as a properties file
17:52 - Volume
Volume
- Storage on local machine
- Or remote, outside of k8s cluster (on cloud or another server)
- Data persistence
- If not, when cluster is restarted, all data(DB,Logs) be gone.
- k8s cluters basically do not manage data persistence
19:46 - Deployment & StatefulSet
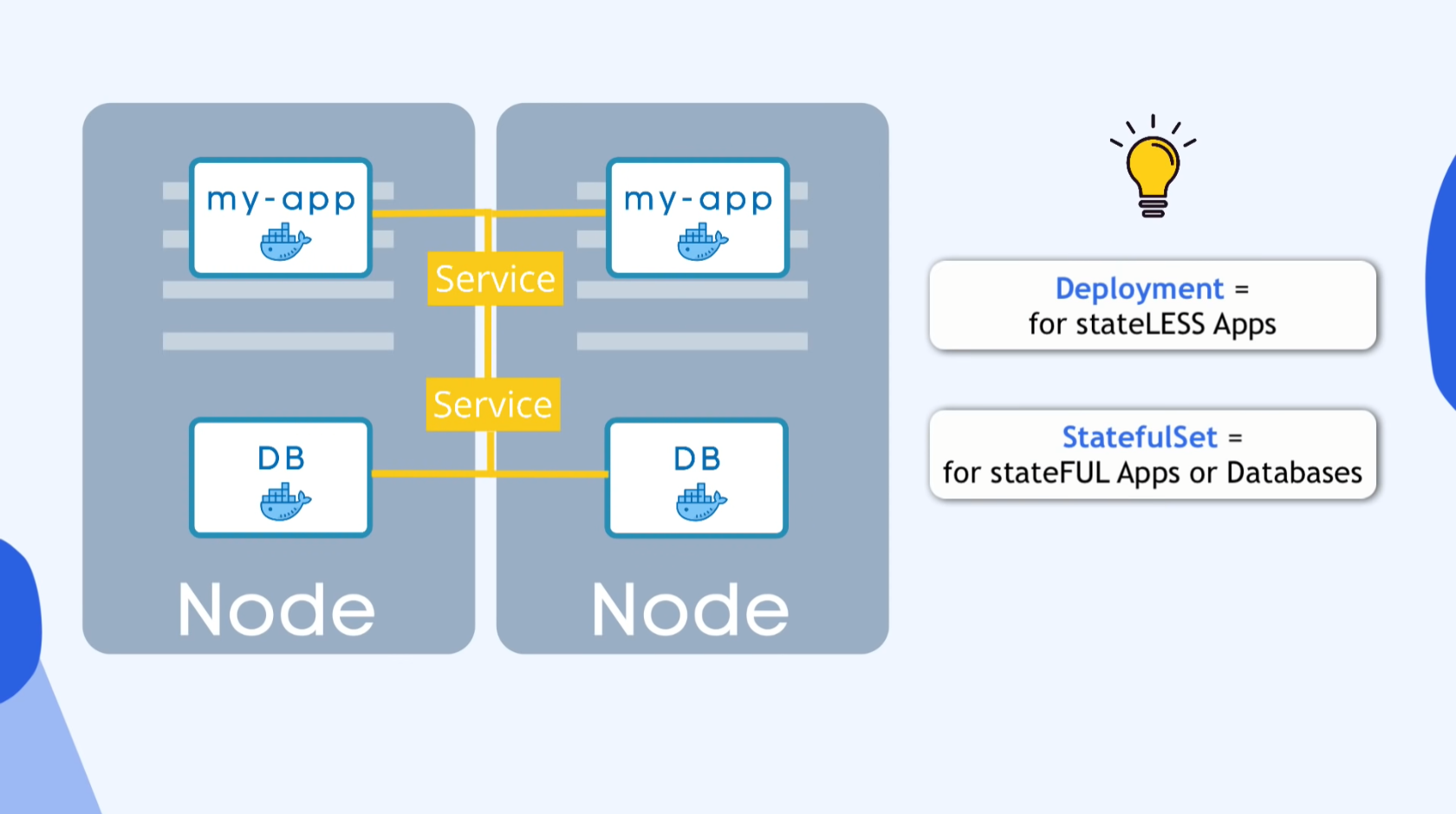
Deployment stage
- In order to avoid downtime,
- Replicate everything on different server
- Replica or Clone is connected to same service
- Service
- Permanent IP
- Load balancer
- Define blueprint for Pods
- Specify how many replicas
DEPLOYMENT
- Blueprint for “my-app”Pods
- You create Deployments
- Abstraction of Pods
DB can’t be replicated via Deployment
- to avoid Data inconsistance
STATEFULSET
- for STATEFUL apps like mysql,elasticsearch,mongodb
Deployment = for stateLESS Apps
StatefulSet = for stateFUL Apps or Databases
Deploying StatefulSet is challenge(not easy)
- DB are often hosted outside of k8s cluster
- k8s cluster communi8s external DB
Wrap up
- Pod
- abstraction of containers
- Service
- Communication
- Ingress
- Route traffic into cluster
- ConfigMap & Secret
- external configuration
- Volume
- Data Persistence
- Deployment & StatefulSet
- Replication the cluster
26:28 - Kubernetes Configuration
K8s conf.
- Master node
- CLI
- kubectl
- API
- YAML, json
- Deployment = a tempalte for creating pods
- replica, container(image),env,prot
- Declarative
- (Actual state) Is == (Desired State) Should
- CLI
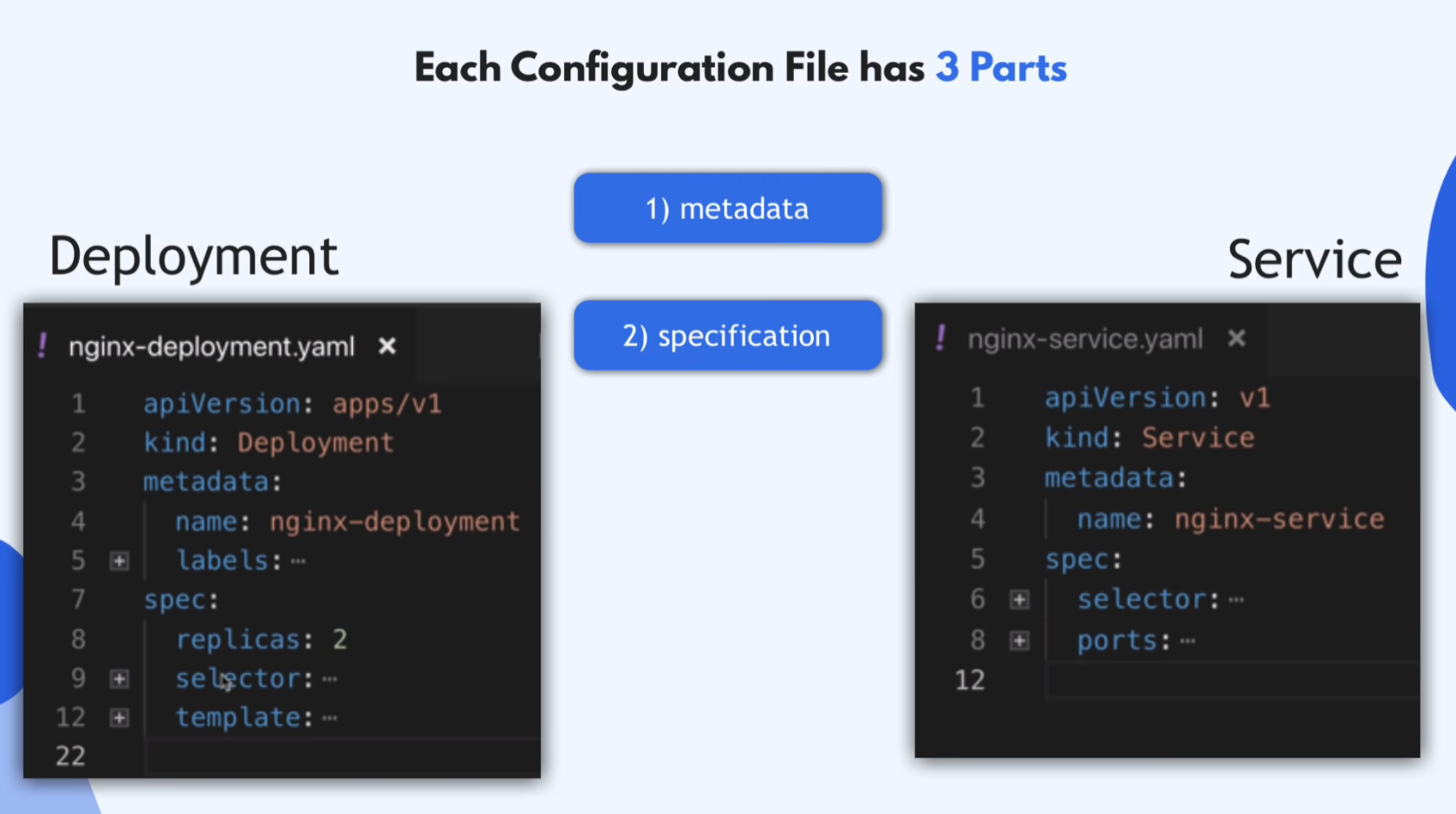
Each Conf. File has 3 Parts
- metadata
- name, labels, …
- specification
- replicas, selector, template / ports, env, …
- attibutes of “spec” are specific to the kind(Depl/Serv)
- status
- Automatically generated and added by k8s
- Compare ‘Desired’ = ‘Actual’?
- k8s updates status continuously
Where does k8s get 3. status data?
- from etcd
- Etch holds the current status of any k8s component
Format of Conf. File
- YAML
- human friendly data serialization standard 4 all prgm Lang.
- syntax: Strict indentation!
- store the conf file w/code version tool(git)
Pod
- 쿠버네티스 클러스터에서 워크로드를 처리하기 위한 리소스의 최소 단위
- 하나 이상의 컨테이너로 구성
- 최소 2개의 컨테이너로 구성(container 네트워크 구성에 필요한 Pause컨테이너)
- 리소스의 상태 조회시에는 1개로 표시됨
- Pause 컨테이너는 내부적인 용도를 위해서 사용되고, 표시되지 않음
- 파드는 여러 노드에 걸쳐 실행될 수 없음 - 단일 노드에서 모든 컨테이너가 구동
- 파드는 일부 속성을 공유함
- 네트워크(IP)
- IP를 공유하며, 각자 포트를 열어서 서비스 가능
- 파드 내 컨테이너 간 통신을 localhost 주소를 사용하여 통신
- 볼륨: 파드에 연결된 볼륨은 모든 컨테이너에서 사용 가능
- 네트워크(IP)
기본 Pod 리소스의 오브젝트 구성
testpod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod
spec:
containers:
- image: c1t1d0s7/myweb
name: test-pod-container
ports:
- protocol: TCP
containerPort: 8080
파드 생성
kubectl create -f <파일명>
kubectl apply -f <파일명>
파드 정보 확인
kubectl get pod [파드이름] // 기본정보 출력
kubectl get pod [파드이름] -o wide // IP, NODE 등 추가정보 출력
kubectl get pod [파드이름] -o yaml // YAML 포맷으로 파드 전체 정보 출력
kubectl describe pod [파드이름] // 파드에 대한 상세정보 출력
파드 및 리소스 세부 필드 확인
kubectl explain <리소스명>
kubectl explain <리소스명>.<필드명>...
로그 확인
kubectl logs <파드이름>
파드로 포트포워딩
kubectl port-forward <파드명> <호스트포트>:<파드포트>
레이블(Label)
- 리소스의 세부항목 중 metadata에 포함
- 키/값 형식을 사용: 값이 반드시 있어야 할 필요는 없음
- 리소스를 식별하기 위한 용도로 사용
- 파드 및 기타 리소스에 광범위하게 사용
- 필수항목은 아님
- 형식: 키이름, 접두사/키이름
- 예시
- release: stable, alpha, beta
- environment: production, dev, qa
- tier: webserver, was, database
레이블을 반영한 파드 생성
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod2
labels:
release: beta
tier: web
spec:
containers:
- image: c1t1d0s7/myweb
name: test-pod-container
ports:
- protocol: TCP
containerPort: 8080
파드에 반영된 레이블 정보 확인
kubectl get pod <파드명> --show-labels kubectl get pod <파드명> -o wide // metadata.labels 항목 kubectl describe pod <파드명> // labels 항목
레이블 변경
kubectl label pod <파드명> <키>=<값> // 없는 키 생성 kubectl label pod <파드명> <키>=<값> --overwrite // 존재하는 키의 값 변경 kubectl label pod <파드명> <키>= --overwrite // 키의 값 삭제 kubectl label pod <파드명> <키>- // 키 삭제
셀렉터(Selector)
검색방식
- 존재 유무: 키가 존재하느냐, 존재하지 않느냐
- 일치성 기준: 같으냐, 같지 않느냐
- 집합성 기준: ~~ 안에 포함되어 있느냐, ~~ 안에 포함되어 있지 않느냐
kubectl 명령 사용시 대상을 식별하는 레이블 조건: -l
-l ‘<키>’ : 키가 존재하는 대상 -l ‘!<키>’ : 키가 존재하지 않는 대상 -l ‘<키>=<값>’ 또는 -l ‘<키>==<값>’ : 키과 값이 일치하는 대상 -l ‘<키>!=<값>’ : 키와 값이 일치하지 않는 대상 -l ‘<키> in (<값1>,<값2>...)’ : 값1, 값2… 안에 키의 값이 해당되는 대상 -l ‘<키> notin (<값1>,<값2>...)’ : 값1, 값2… 안에 키의 값이 해당되지 않는 대상
어노테이션(Annotations)
- label과 유사하게 키/값 구조를 가지는 데이터
- 개체 식별용도로 사용하지 않음
- 부가적인 설명 등이 필요한 항목 기술
- 리소스 관련 기본 정보
- 모니터링 관련 정보
- 디버깅 정보
- 다른 요소와의 관련 정보
- 책임자 등
- 쿠버네티스 클러스터 내에서 API서버 및 다른 요소에서 참고하는 용도로 사용
annotation 예시
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod3
annotations:
developer: Michael Jackson
manager: Bill Gates
spec:
containers:
- image: c1t1d0s7/myweb
name: test-pod-container
ports:
- protocol: TCP
containerPort: 8080
네임스페이스(Namespace)
쿠버네티스 내 리소스를 논리적으로 분리
기본적으로 생성되어 있는 네임스페이스
- kube-node-lease: 쿠버네티스 노드의 가용성을 체크하기 위한 리소스용
- kube-public: 기본적으로 생성되어 모든 사용자가 읽기 권한으로 접근 가능한 네임스페이스. 일반적으로 사용하지 않음
- kube-system: 기본적인 쿠버네티스 클러스터의 리소스(컨트롤플레인)
- default: 기본적으로 생성된 사용자용 네임스페이. 기본값
네임스페이스 리소스 파일 예시
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: my-private-namespace
네임스페이스 생성
- 오브젝트 파일 사용
kubectl create -f mynamespace.yaml - 명령 사용
kubectl create namespace mynamespace
네임스페이스에 리소스 생성
- 리소스 정의 내에 네임스페이스 지정: .metadata.namespace
… metadata: name: testpod namespace: mynamespace … - 생성 명령 실행 시 네임스페이스 지정:
kubectl create -f testpod.yaml –namespace mynamespace -
- kubectl 명령 사용환경에서 기본 네임스페이스 지정
- ServiceAccount 부분에서 확인예정
Pod
파드의 생명주기 / Probe
파드의 내부 항목 중 .status.phase : 현재 파드의 상태 표시
파드의 상태 종류 Pending 스케줄링 되기 전 파드가 스케줄러에 의해 승인은 되었으나 아직 실행 전 스케줄링 후 생성되었으나 이미지 pull 중인 상태 Running 현재 정상적으로 실행중인 상태 컨테이너가 구동중인 상태 시작된 상태 / 재시작중인 상태 Succeeded 재시작되도록 지정되지 않은 파드가 정상적으로 종료되었을 때 Failed 정상적이 아닌 상태로 종료되었을 때 Unknown 파드의 상태를 파악할 수 없을 때(노드와의 통신 오류 등)
파드 내 컨테이너의 상태 Waiting Running, Terminated이 아닌 상태 만들어지는 중 Reason 항목에 세부 이유 표시됨 Running 실행중 Terminated 오류 등에 의하여 중지 된 상태 Reason 항목에 세부 이유 표시됨
재시작 정책 apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: test-pod spec: restartPolicy: Always containers:
- image: c1t1d0s7/myweb
name: test-pod-container
ports:
- protocol: TCP containerPort: 8080 apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: hello-world spec: containers:
- name: hello-world-container image: hello-world apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: hello-world2 spec: restartPolicy: Never containers:
- name: hello-world-container image: hello-world apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: hello-world3 spec: restartPolicy: OnFailure containers:
- name: hello-world-container image: hello-world apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: false-pod spec: containers:
- name: false-pod-container image: ubuntu command: [“false”] restartPolicy: OnFailure
기본 파드의 정상/비정상 판단 방식 컨테이너의 프로세스가 정상적으로 종료/실행중 : 정상 컨테이너의 프로세스가 비정상종료: 비정상
사용자의 설정에 따른 정상 비정상 판단 방식 : Probe
Probe의 종류 Liveness Probe Readiness Probe Startup Probe
Liveness Probe 현재 파드가 정상 동작하고있는가 판단하는 Probe 별도의 판단기준을 설정하여 정상 여부를 체크 (다른 probe도 동일) 특정 경로로 http GET 요청 전송 2xx, 3xx 등의 응답을 수신할 경우 정상 httpGet TCP Socket 연결을 통해 정상 여부를 체크 3way handshake 과정이 정상적으로 수립되는지 확인 tcpSocket 테스트를 위한 명령을 별도로 수행 명령 실행의 종료상태에 따라 확인 exec
Liveness Probe 예시 apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-liveness-1 spec: containers:
- name: pod-liveness-1-container
image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb
ports:
- containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP Liveness Probe 미적용
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-liveness-2 spec: containers:
- name: pod-liveness-2-container
image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb
ports:
- containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health port: 8080 Liveness Probe 적용
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-liveness-3 spec: containers:
- name: pod-liveness-3-container
image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb
ports:
- containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /health?code=404 port: 8080 Liveness Probe 적용
실습용 컨테이너 이미지 활용 curl -v 192.168.9.70:8080/health // health check용으로 200 응답 curl -v 192.168.9.70:8080/health?code=404 // 지정한 code 응답
Startup Probe 컨테이너 구동 후 시작된 상태임을 체크하는 probe startup probe의 테스트를 통과한 이후에야 컨테이너가 구동중으로 판단 startup probe 테스트 통과 전까지 다른 probe가 동작하지 않음
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: pod-startup spec: containers:
- name: pod-startup-container
image: ubuntu
command: [“sleep”,”infinity”]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP livenessProbe: exec: command: [“test”, “-f”, “/tmp/test2”] startupProbe: exec: command: [“test”, “-f”, “/tmp/test1”] Liveness Probe + Startup Probe 적용 kubectl exec pod-startup – touch /etc/test1 kubectl exec pod-startup – touch /etc/test2 // 체크에 사용되는 파일 생성 후에는 파드 이상없이 Running 동작
참고) HTTP Method 현재 가장 많이 사용되고 있는 HTTP 1.1 버전
HTTP 요청시 사용한 방식 : Method GET 서버에게 요청한 페이지를 달라고 할 경우 요청하고자 하는 서버의 페이지 정보를 요청(경로) 보낼 내용을 URL의 파라미터로 전송 POST 서버에게 데이터를 전달할 경우 요청을 전송하고 응답 받음 보낼 내용을 HTTP BODY에 필요한 내용을 집어넣어 전송 HEAD 서버의 응답 헤더만을 요청할 경우
HTTP Status code 404 - Not Found
1xx : continue 2xx : 정상 처리된 경우(200, OK) 3xx : 일시적/영구적 변경이 있을 경우 4xx : 에러(클라이언트 에러)- 요청이 잘못됨(없는 자원 요청, 권한없음) 5xx : 에러(서버 에러) - DB연결 에러, DB 처리 에러
컨트롤러 파드 단위로 관리하는 것이 아닌, 컨트롤러를 통해 파드를 관리 파드의 복제본을 생성하여 다수의 파드를 관리
컨트롤러 레플리케이션 컨트롤러 Replication Contoller 레플리카셋 ReplicaSet 데몬셋 DaemonSet 잡 Job 크론잡 CronJob 디플로이먼트 Deployment 스테이트풀셋 StatefulSet
레플레이케이션 컨트롤러 앞으로는 없어질 예정 레플리카셋이 그 자리를 대체 파드의 복제본을 생성 파드의 개수를 유지하는 동작
레플리케이션 컨트롤러 예시 apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: test-rc spec: replicas: 3 selector: app: myweb template: metadata: labels: app: myweb spec: containers: - name: myweb-container image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP
레플리케이션 컨트롤러 레이블 테스트 testpod.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: testpod labels: app: myweb spec: containers:
- name: testpod-container image: c1t1d0s7/myweb
레플리카셋 (ReplicaSet) 레플리케이션 컨트롤러와 동일한 동작을 수행 차이점: 셀렉터 조건이 다름 레플리케이션 컨트롤러: 일치성 기준 <키>=<값> 레플리카셋: 일치성 기준 + 존재유무 + 집합성기준
레플리카셋 apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: ReplicaSet metadata: name: test-rs spec: replicas: 3 template: metadata: labels: app: myweb spec: containers: - name: myweb-container image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: ReplicaSet metadata: name: test-rs spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: myweb template: metadata: labels: app: myweb spec: containers: - name: myweb-container image: ghcr.io/c1t1d0s7/go-myweb ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP
셀렉터 형식
일반적인 키=값 일치성 조건 selector: matchlabels: 키 존재유무 (키가 있을 때) selector: matchExpressions: - key: <키> operator: Exists // 키가 존재할 때 키 존재유무 (키가 없을 때) selector: matchExpressions: - key: <키> operator: DoesNotExists // 키가 존재할 때 레이블의 집합성 조건 만족여부 (대상 중 포함될 때) selector: matchExpressions: - key: <키> operator: In values: - <값1> - <값2> - … 레이블의 집합성 조건 만족여부 (대상 중 포함되지 않을 때) selector: matchExpressions: - key: <키> operator: NotIn values: - <값1> - <값2> - …
matchExpressions 사용시 여러 조건을 AND(&)의 형식으로 함께 적용 가능 selector: matchExpressions:
<첫 번째="" 조건=""> <두 번째="" 조건="">
Leave a comment