220513 Today I Learned
일지
특이사항없음
의욕도 없음
주요 키워드
오늘의 할일
- 220513 TIL 작성
- Udemy 4회 풀기
- 쿠버네티스 사전준비
- 도커/쿠버네티스 교재읽기
추가로 정리해야할 부분
수업 정리
Kubernetes Crash Course for Absolute Beginners
0:00 - Intro and Course Overview
Overview
Part 1. Introdunction to k8s
- What is k8s
- why do we need it.
- why did it become polular.
- k8s Architecture
- How they works in background
Part 2. Main k8s Components
- Pod
- Volume
- Service
- Ingress
- ConfigMap
- Deployment
- Secret
- StatefulSet
- DaemonSet
Part 3. Local Setup
Part 4. Demo Project
k8s is very popular & complex
1:44 - What is Kubernetes
Official def. of k8s
- Open source container orchestration tool
- Devoped by Google
- Helps manage containerized apps in diffrent deploy environment.
What prbls k8s solves?
What are the tasks of an orch. tools?
- Neeed for con. orch. tool
- Trend from Monolith to Microservices.
- Increase usage of (small,independent) con.
- Demand for a proper way of managing those hunds of con.
What features orch tools offer?
- High Availability or no downtime
- Scalability or high performance
- Disaster recovery - backup&restore
4:33 - Kubernetes Architecture
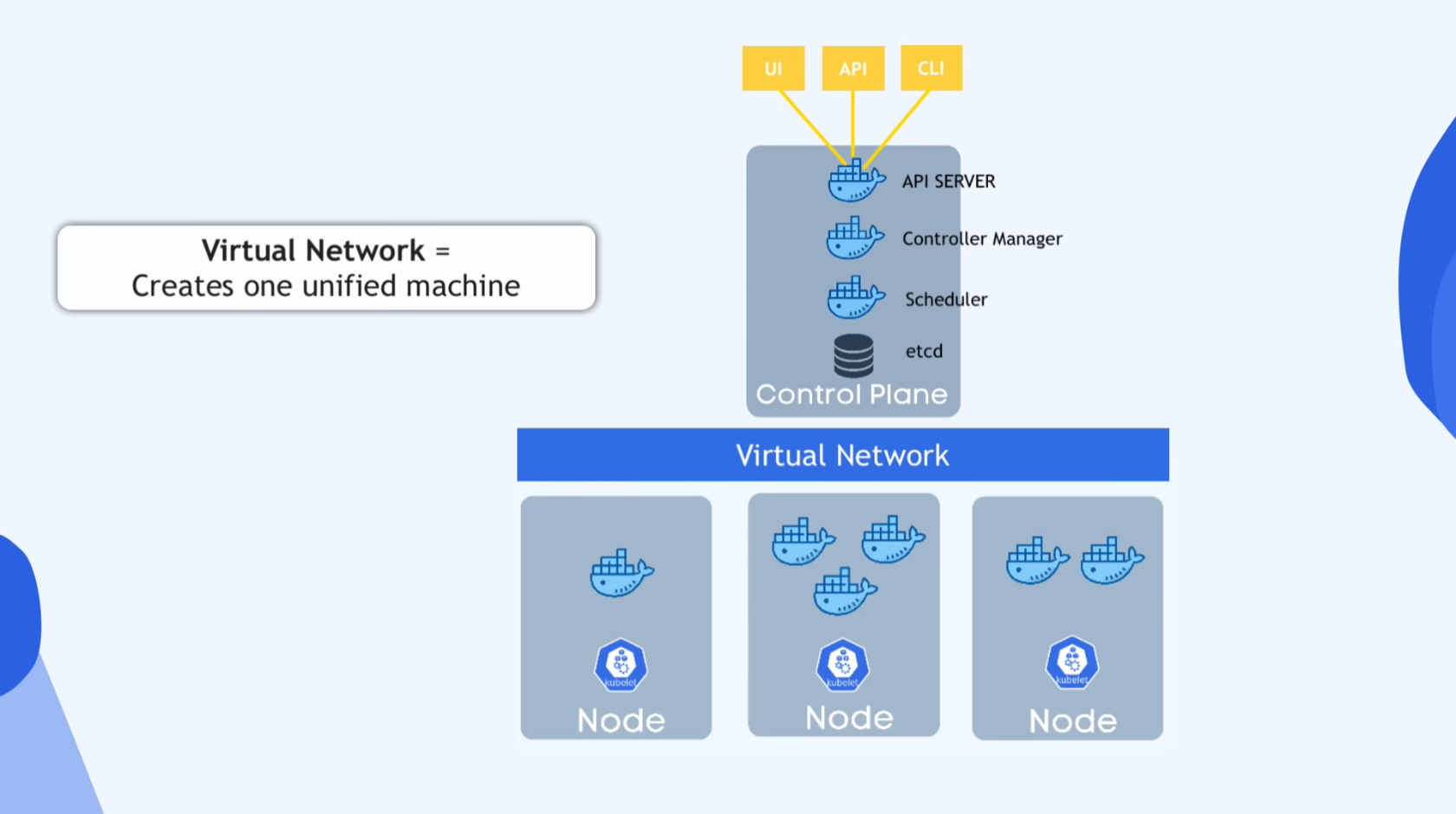
at least one Master node (Virtual/Physical)
- several k8s processes
- necessary to run&manage the cluster
- API server
- Entrypoint to k8s cluster
- UI: Dashboard, etc
- API: scripts&automating
- CLI
- Entrypoint to k8s cluster
- Controller Manager
- Keep track of happenings in cluster
- Scheduler
- ensures Pods placement
- Scheduler decides on which node new pod should be scheduled based on Load
- etcd storage
- k8s backing store
Virtual Network
- Master and Workers talks on N/W
- Creates 1 unified mach. inside of a cluster
several Worker nodes
- a kubelet process
- kubelet: k8s process that communic8s each nodes&excutes some commands
- containers of diffrent apps
- the place that apps r running
| Master | Worker |
|---|---|
| small master processes | Higher workload |
| IMPORTANT | bigger&more resources |
| Need Redundance | - |
8:58 - Main K8s Components
09:29 - Node & Pod
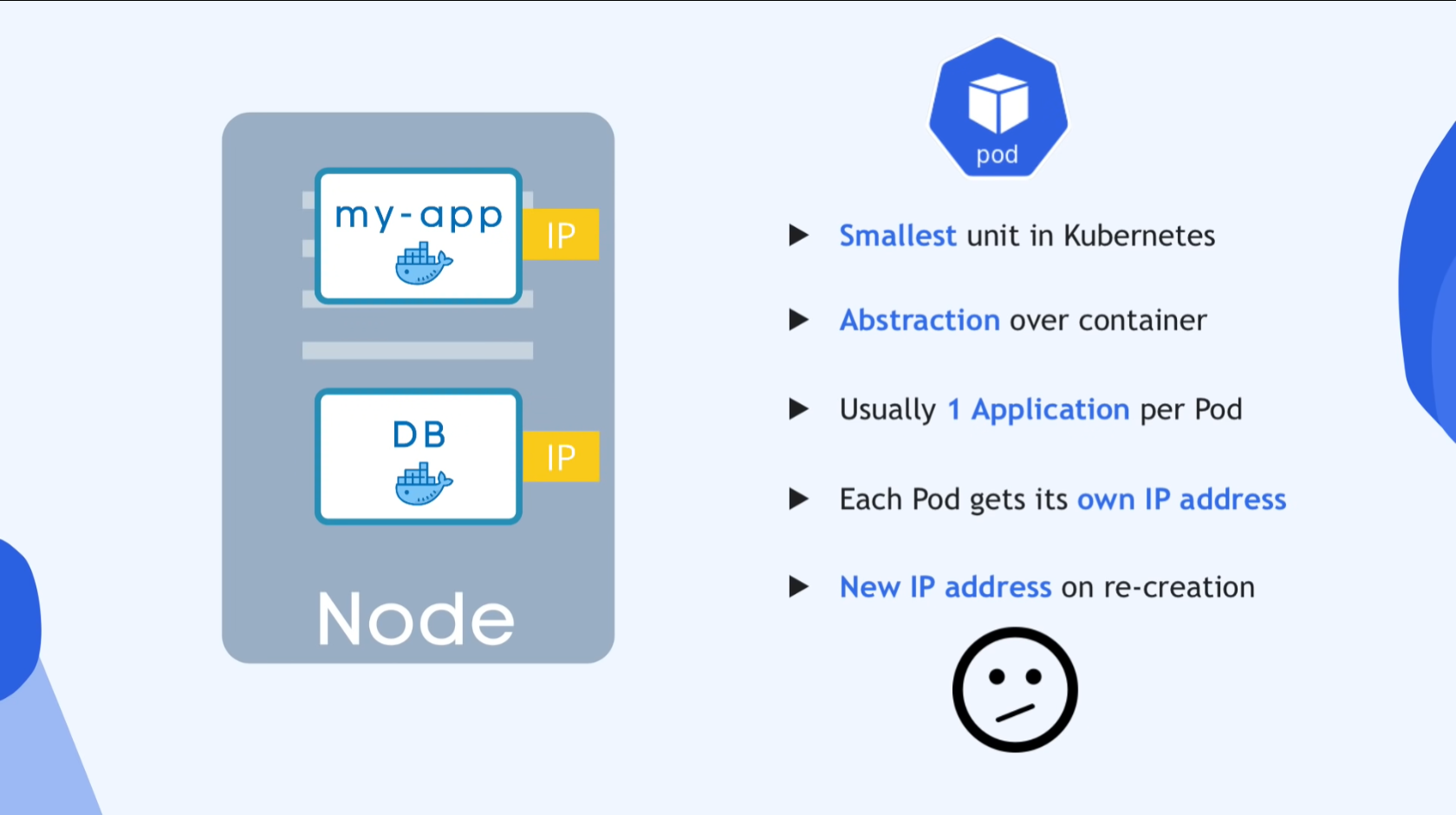
Pod
- Smallest unit in k8s
- Abstraction over container
- Top layer of image
- Usually 1 app per Pod
- Each Pod get its own IP addr
- talks using internal IP
- Ephemeral
- New IP addr on re-creation
- Inconvenient based on IP structure
12:19 - Service & Ingress
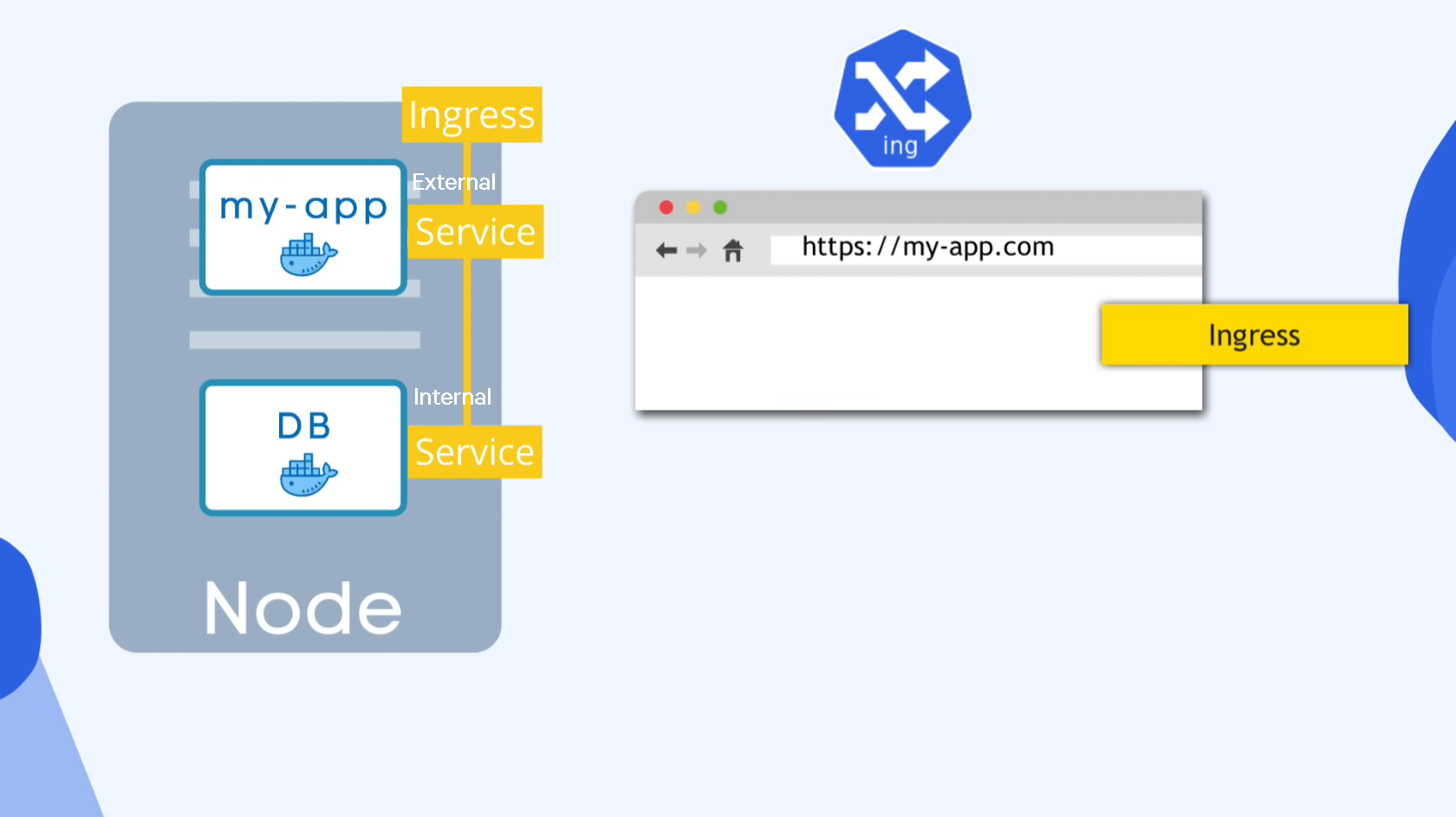
Service
- Permanent IP addr
- Lifecycle of Pod and Service NOT CONNECTED
- Specify the type of Service on creation
- Internal Service = Default
- External Service
- user can access app on web browser
- Internal Service
- user cannot access db
Ingress
- node-ip:port 주소 형식은 실제 사용엔 무리가 있음
- 일종의 도메인서버역할인듯?
- my-app.com 식으로 전환
14:31 - ConfigMap & Secret
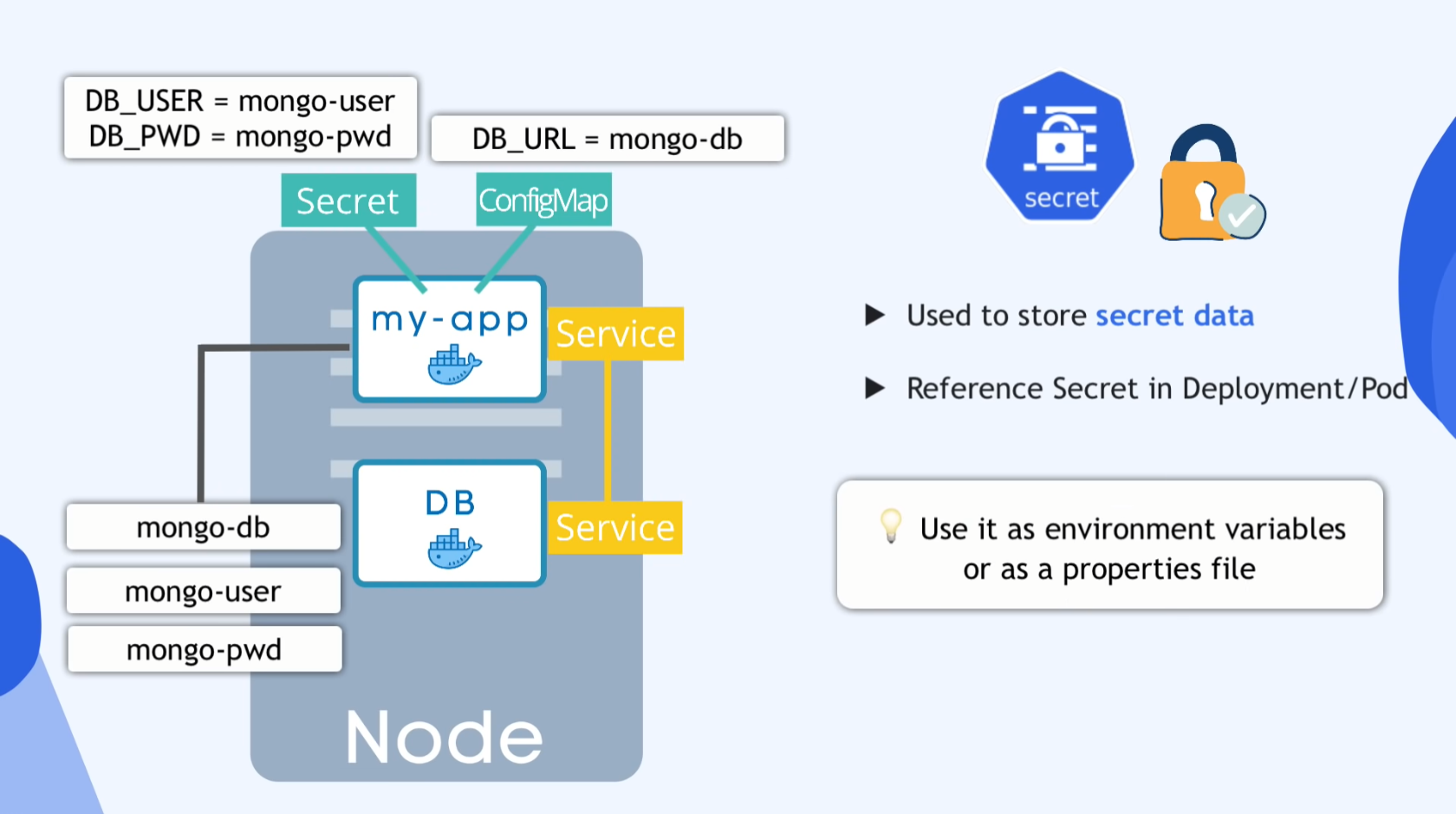
Database URL usually in the BUILT apps
- If u change the DB Endpoint
- Rebuild the image
- Push it to repo
- Pull it in Pod
- Restart whole procedure
ConfigMap
- External conf. of apps
- DB_URL
- DB Servicename
- DB username
- DB password
- ConfigMap is for non-credential data only!
Secrets
- Used to store secret data
- Reference Secret in Deployment/Pod
Use it as environment variables or as a properties file
17:52 - Volume
Volume
- Storage on local machine
- Or remote, outside of k8s cluster (on cloud or another server)
- Data persistence
- If not, when cluster is restarted, all data(DB,Logs) be gone.
- k8s cluters basically do not manage data persistence
19:46 - Deployment & StatefulSet
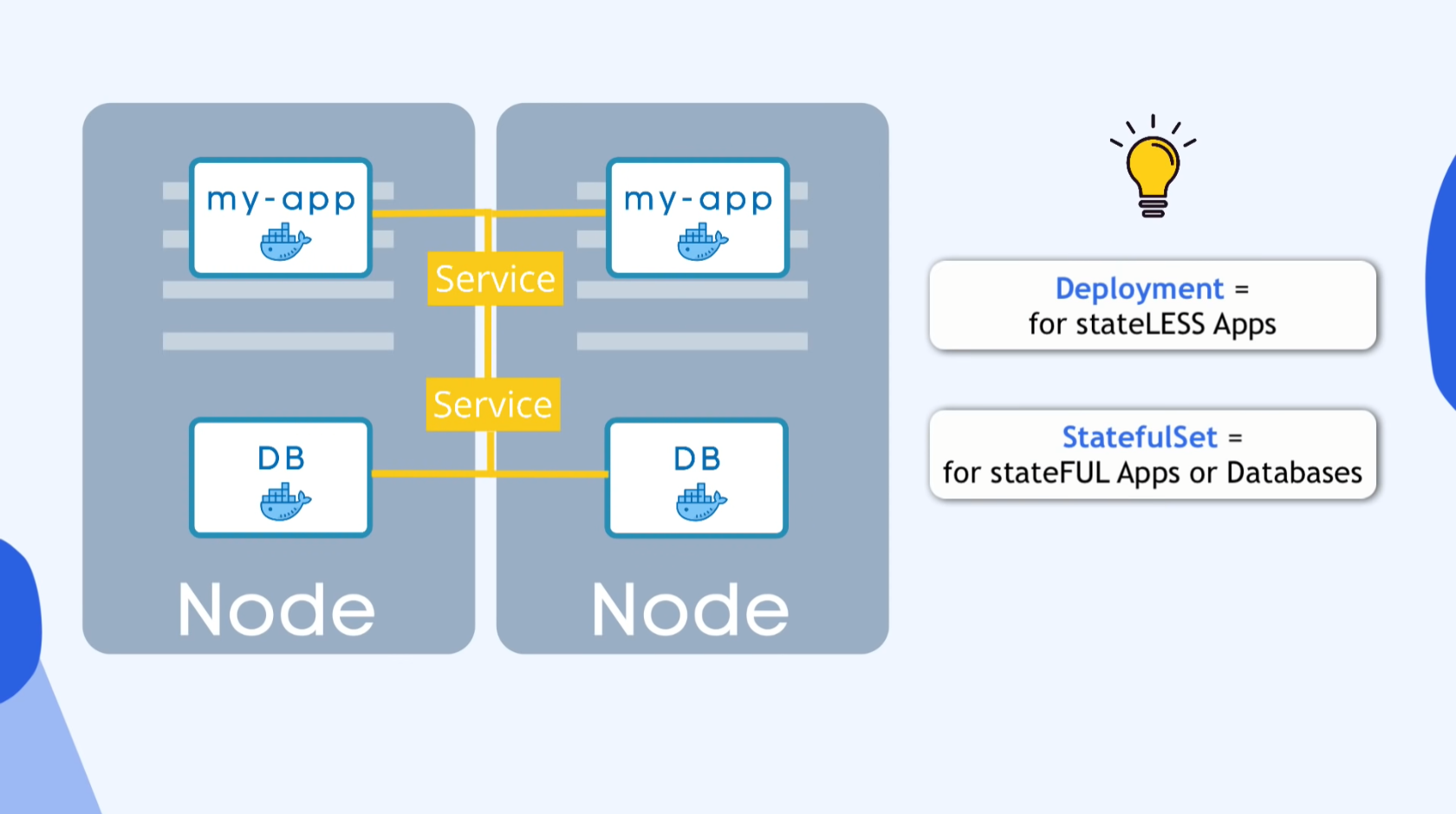
Deployment stage
- In order to avoid downtime,
- Replicate everything on different server
- Replica or Clone is connected to same service
- Service
- Permanent IP
- Load balancer
- Define blueprint for Pods
- Specify how many replicas
DEPLOYMENT
- Blueprint for “my-app”Pods
- You create Deployments
- Abstraction of Pods
DB can’t be replicated via Deployment
- to avoid Data inconsistance
STATEFULSET
- for STATEFUL apps like mysql,elasticsearch,mongodb
Deployment = for stateLESS Apps
StatefulSet = for stateFUL Apps or Databases
Deploying StatefulSet is challenge(not easy)
- DB are often hosted outside of k8s cluster
- k8s cluster communi8s external DB
Wrap up
- Pod
- abstraction of containers
- Service
- Communication
- Ingress
- Route traffic into cluster
- ConfigMap & Secret
- external configuration
- Volume
- Data Persistence
- Deployment & StatefulSet
- Replication the cluster
26:28 - Kubernetes Configuration
K8s conf.
- Master node
- CLI
- kubectl
- API
- YAML, json
- Deployment = a tempalte for creating pods
- replica, container(image),env,prot
- Declarative
- (Actual state) Is == (Desired State) Should
- CLI
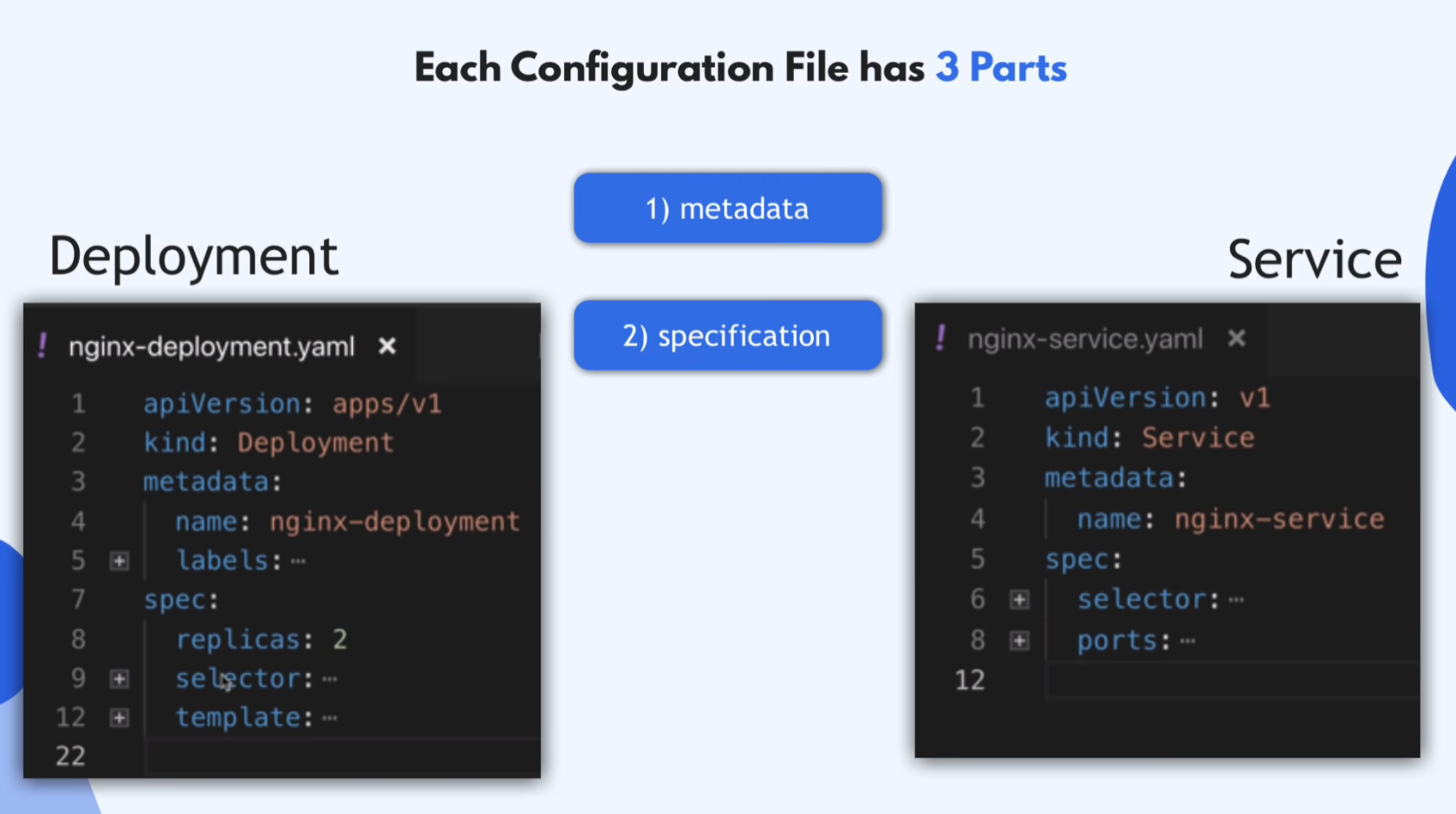
Each Conf. File has 3 Parts
- metadata
- name, labels, …
- specification
- replicas, selector, template / ports, env, …
- attibutes of “spec” are specific to the kind(Depl/Serv)
- status
- Automatically generated and added by k8s
- Compare ‘Desired’ = ‘Actual’?
- k8s updates status continuously
Where does k8s get 3. status data?
- from etcd
- Etch holds the current status of any k8s component
Format of Conf. File
- YAML
- human friendly data serialization standard 4 all prgm Lang.
- syntax: Strict indentation!
- store the conf file w/code version tool(git)
32:39 - Minikube and Kubectl - Setup K8s cluster locally
Production Cluster Setup
- Multiple Master & Worker nodes
- Separate virtual or physical machines
- Test on local machine?
Minikube
- Master and Node processes run on ONE mach.
- Docker pre-installed
Kubectl
- command line tool for k8s cluster
- Most powerful among UI, API, CLI(=kubectl)
- Can interacts w/Cloud cluster
설치과정은 Mac용이야 흑흑
kubectl CLI > for conf. the Minikube cluster Minikube CLI > for start up/delte the cluster
41:17 - Complete Demo Project: Deploy WebApp with MongoDB
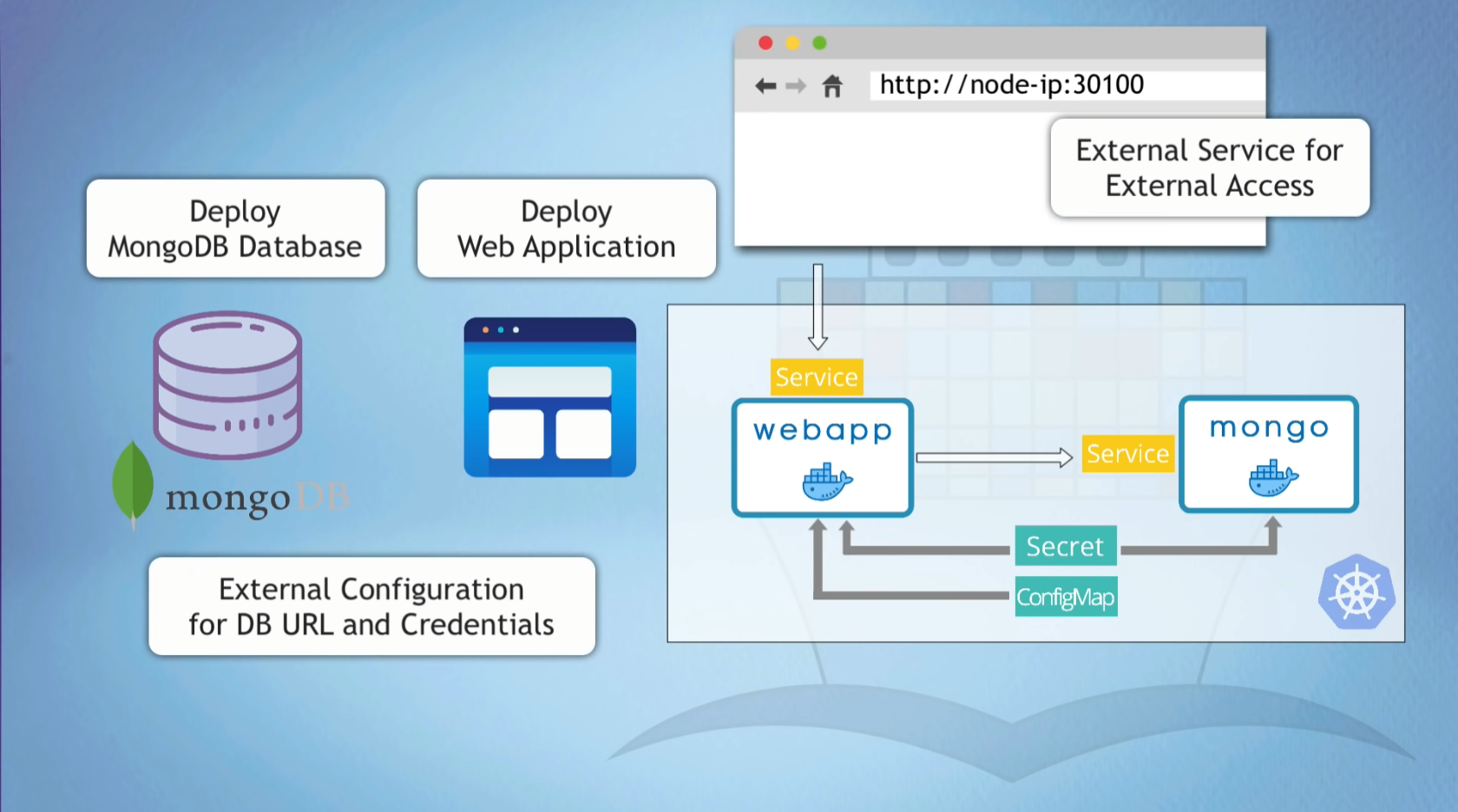
k8s Components Overview
- Create 4 k8s conf files
- ConfigMap; MongoDB Endpoint
- Secret; MongoDB User & Pwd
- Deployment\&Service; MongoDB App w/Internal Service
- Deployment\&Service; Wepapp w/External Service
# mongo config
##### 1:05:40 - Interacting with Kubernetes Cluster
##### 1:11:03 - Congrats! You made it to the end 🎉
---
AWS ECR ECR(Elastic Container Registry): AWS에서 제공하는 컨테이너 저장소 ECR 사용하
aws cli를 사용하여 패스워드 확인 중 오류 발생 시 (시간 정보) [root@docker ~]# yum -y install chrony [root@docker ~]# systemctl start chronyd.service [root@docker ~]# timedatectl set-ntp true
aws ecr 로그인 패스워드 확인
aws configure // aws 계정 access key 및 secret key 입력
aws ecr get-login-password // 패스워드 출력
aws ecr 로그인
aws ecr get-login-password | docker login –username AWS –password-stdin

Leave a comment